(Ubuntu) Linux Starter Pack
This content is open source. Help improve it.
I’ve found myself repeating, and having a hard time remembering all of the steps when setting up ubuntu. Over the past 3 years, I started with Mint, as a daily driver, and have moved on to Ubuntu 19.04, and 18.04 LTS.
This is now where I’ll be keeping track of this info. Over time, I’ll organize this better, and add some notes for context, and mean to walk through the first steps of a few different setups.
At the moment, this is just a loosely organized collection of links I found useful, and leads for further exploration.
Gnu
- Linux and the GNU System
Many computer users run a modified version of the GNU system every day, without realizing it. Through a peculiar turn of events, the version of GNU which is widely used today is often called “Linux”, and many of its users arenot aware that it is basically the GNU system, developed by the GNU Project.
- The GNU Manifesto - GNU Project - Free Software Foundation
I consider that the Golden Rule requires that if I like a program I must share it with other people who like it. Software sellers want to divide the users and conquer them, making each user agree not to share with others. I refuse to break solidarity with other users in this way. I cannot in good conscience sign a nondisclosure agreement or a software license agreement. For years I worked within the Artificial Intelligence Lab to resist such tendencies and other inhospitalities, but eventually they had gone too far: I could not remain in an institution where such things are done for me against my will.
So that I can continue to use computers without dishonor, I have decided to put together a sufficient body of free software so that I will be able to get along without any software that is not free. I have resigned from the AI Lab to deny MIT any legal excuse to prevent me from giving GNU away.(2)
- Overview of the GNU System - GNU Project - Free Software Foundation
The word “free” in “free software” pertains to freedom, not price. You may or may not pay a price to get GNU software. Either way, once you have the software you have four specific freedoms in using it. The freedom to run the program as you wish; the freedom to copy the program and give it away to your friends and co-workers; the freedom to change the program as you wish, by having full access to source code; the freedom to distribute an improved version and thus help build the community. (If you redistribute GNU software, you may charge a fee for the physical act of transferring a copy, or you may give away copies.)
The project to develop the GNU system is called the “GNU Project”. The GNU Project was conceived in 1983 as a way of bringing back the cooperative spirit that prevailed in the computing community in earlier days—to make cooperation possible once again by removing the obstacles to cooperation imposed by the owners of proprietary software.
- What’s in a Name?
A great challenge to the future of free software comes from the tendency of the “Linux” distribution companies to add nonfree software to GNU/Linux in the name of convenience and power. All the major commercial distribution developers do this; none limits itself to free software. Most of them do not clearly identify the nonfree packages in their distributions. Many even develop nonfree software and add it to the system. Some outrageously advertise “Linux” systems that are “licensed per seat”, which give the user as much freedom as Microsoft Windows.
People try to justify adding nonfree software in the name of the “popularity of Linux”—in effect, valuing popularity above freedom. Sometimes this is openly admitted. For instance, Wired Magazine said that Robert McMillan, editor of Linux Magazine, “feels that the move toward open source software should be fueled by technical, rather than political, decisions.” And Caldera’s CEO openly urged users to drop the goal of freedom and work instead for the “popularity of Linux”.
- GNU/Linux FAQ by Richard Stallman
Distro
- Is Ubuntu 19.04 worth upgrading to from 18.04 LTS? - Quora
Thanks for the A2A. No, it’s not. And it’s not recommended either. First of all, Ubuntu likes to play around a lot. For example, 18.10 uses Wayland. Also, Ubuntu likes to delete your manually installed packages upon upgrade (see my other answers f…
- Installing Ubuntu 18.04 “Bionic Beaver” For i386
- Fix No Bootable Device Found Error After Installing Ubuntu - It’s FOSS
- Linux Mint vs Ubuntu: Detailed Comparison
If you’re looking for a new Linux distro for your desktop, then you must have stumbled upon Linux Mint and Ubuntu. They are the two most popular desktop Linux distros.
Both Linux Mint and Ubuntu have several editions (flavors) to choose from, so we’ll have them in mind while doing this comparison.
- Ubuntu vs. Debian vs. Mint - which one do you feel is best?
Please keep in mind privacy, system integrity, ease of use for noobs, etc. Curious for thoughts from the community.
Setup
Boot Loaders and Partition Tables
Basically all new systems use UEFI. However, if you are shopping for old laptops, or simply installing linux on some old windows machine you have laying around, then you might run into the legacy setup. The deal is how they are partitioned, MBR vs GPT, and can depend upon your BIOS. So it matters to figure out from the beginning what your system requirements are.
Actually, when I first installed linux, I just hit the install button, and the installer did its magic. It was only later, I puzzled for quite some time over this matter, when trying to “properly” set up a fresh system, not just letting the installer do all the work.
- MBR VS GPT, which is the best choice for your computer?
- If the motherboard on your computer supports UEFI (Unified Extensile Firmware), you can choose GPT.
- If the motherboard uses legacy BIOS system, you should choose MBR. BIOS does not support GPT-partitioned volumes.
- Explaining UEFI Firmware for Linux Users - LinuxBabe
You will see online that many people refer to it as UEFI BIOS. Strictly speaking, this is wrong, because BIOS is not a generic term for firmware. BIOS is a specific firmware for IBM compatible PC, so we should call the newer firmware UEFI.
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UEFI
The Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) or its version 2.x variant, Unified EFI (UEFI) is a firmware type that is widespread on recent computers, especially those more recent than 2010. It is intended to replace the traditional BIOS firmware that is prevalent on earlier machines. This page provides information about installing and booting Ubuntu using UEFI, as well as about switching between UEFI mode and legacy BIOS mode using Ubuntu. Warning /!\ Most modern computers support both UEFI mode and BIOS mode.
- How to create an EFI System Partition?
- help.ubuntu.com/community/Installation/UEFI-and-BIOS
- Legacy Bios, UEFI and SecureBoot ready Ubuntu Live image customiza…
- How can I reinstall GRUB to the EFI partition?
- rhboot/efibootmgr
- Managing EFI Boot Loaders for Linux: CSM: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
- How do multiple boot loaders work on an EFI system partition
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Boot-Repair
- Ubuntu installer now supports ZFS on the boot partition
Partitions
- Partitions: Planning Your Linux Installation
- How I am partitioning the HDD for Linux setup.
- Gparted - GNOME Partition Editor
- Causing ZFS corruption for fun, profit, and quality assurance
Install Media
- How to verify a file using an asc signature file? As an example, this project offers an *.asc file with a PGP signature to verify the contents of the download (as opposed to a checksum, you can see the empty column): https://ossec.github.io/downlo…
- How to Verify a Download in Ubuntu with SHA256 Hash or GPG Key
You may have often downloaded some open source software, for instance, various Linux distributions ISO. While downloading, you might also notice a link to download checksum file. What is that link for? Actually, Linux distributions distribute checksum files along with
- 1. How to create a bootable Linux usb stick (mac) (playlist also includes video for creating linux virtual machine)
Configuration
How do I configure swappiness? How to add a directory to the PATH? How To Set Up a Firewall with UFW on Ubuntu 18.04
By default, Ubuntu comes with a firewall configuration tool called UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall). UFW is a user-friendly front-end for managing iptables firewall rules and its main goal is to make managing iptables easier or as the name says uncomplicated. Ubuntu 12.10 “Turn screen off when inactive for: Never” still turn… How to install executables
- Things To Do After Installing Ubuntu
- 20 Things to do After Installing Ubuntu 18.04 and 18.10
- Initial Server Setup with Ubuntu 18.04
When you first create a new Ubuntu 18.04 server, there are a few configuration steps that you should take early on as part of the basic setup. This will increase the security and usability of your server and will give you a solid foundation for subseq
- How to install a deb file, by dpkg -i or by apt?
I have a deb package for installation. Shall I install by dpkg -i my.deb, or by apt? Will both handle the software dependency problem well? If by apt, how can I install from the deb by apt?
- How to mount a new drive on startup
- How can I install a package without root access?
- Install Media Codecs
sudo add-apt-repository multiversesudo apt install ubuntu-restricted-extras
Install:
vlc, pinta, vscode, keepassxc, git, ssh\gpg
Install walpapers from old releases of ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-wallpapers-* edgy-wallpapers feisty-wallpapers gutsy-wallpapers
Dotfiles
- Understanding Linux configuration files
This article explains configuration files on a Linux system that control user permissions, system applications, daemons, services, and other administrative tasks in a multi-user, multi-tasking environment. These tasks include managing user accounts, allocating disk quotas, ma…
- Getting Started With Dotfiles
- dotfiles.github.io
- The Rabbithole Series, Part 1
- logind.conf.5.en.html
The default configuration is defined during compilation, so a configuration file is only needed when it is necessary to deviate from those defaults. By default, the configuration file in /etc/systemd/ contains commented out entries showing the defaults as a guide to the administrator. This file can be edited to create local overrides.
Accounts and Permissions
I was having a bit of trouble understanding how to properly set up and operate a user alongside and admin acct
I guess the idea is that the administrator account is the first created automatically (in ubuntu) then create a user account. Although the default administrator requires password for sudo, since ‘root’ is actually abstracted from the ui. Though not actually root, that administrator does, have generally elevated privs otherwise. So by making a user account, you have an additional layer of security, should some application get loose, it doesn’t inherit any administrator privliges from you
but……… to use sudo from the user account
you must either su administrator or add the user account to your list of sudoers
and if you break sudo by messing up /etc/sudoers then you can use pkexec as an alternative to sudo to fix it
- How to create sudo user on Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver Linux - Linu…
- Accessing sudo from a non-administrator profile
- How do I add a user to sudoers file?
If you want to add another user or if your username did not install Ubuntu, then you must log in as that user who installed Ubuntu, enter sudo -i to get root prompt; and then enter this command visudo.
I usually add the users I want to have sudo access. You can also add a group to have sudo access. I prefer just adding the users. I added a space in between the following, so it would format better.
# User_Alias ADMINS = jsmith, mikemdbadmin ALL=(ALL) ALLYou can also use this command (as root)
sudo usermod -a -G sudo hduser - How to allow non-superusers to mount any filesystem?
Is it possible to allow some particular users (e.g. members of a group) to mount any filesystem without superuser privileges on Linux? Another question might have been “in what ways a user can har…
- How can I mount partitions in Thunar without password?
- How To Create a Sudo User on Ubuntu [Quickstart]
The sudo command provides a mechanism for granting administrator privileges, ordinarily only available to the root user, to normal users. This guide will show you the easiest way to create a new user with sudo access on Ubuntu, without having to modif
- How can I run an application with a GUI as admin from a non-admin …
I defined 2 user accounts: one with admin privilege (with sudo right) => lets call it adminuser. a 2nd one without any privilege => lets call it normaluser and I configure the autologin on this 2n…
- Removing Root Login And Other First Steps Ubuntu
- The Ultimate Guide to Linux Users, Groups, and Permissions
Everything you need to know about Linux users, groups, and permissions. Learn about Linux users including system users and regular users, switching to the root user, adding users, removing users, the difference between sudo and su, changing permissions, changing ownership w…
- Understanding Linux Permissions
Desktop
- Customize Ubuntu 18.04 GNOME With These Simple Tips
- How To Change The GTK, Icon Or GNOME Shell Theme In GNOME
- How To Make Your Ubuntu Desktop Faster
- Rotating screen in Ubuntu and Linux Mint
- Top 20 GNOME Extensions You Should Be Using Right Now
You can enhance the capacity of your GNOME desktop with extensions. Here, we list the best GNOME extensions to save you the trouble of finding them on your own.
- Customize Ubuntu 18.04 GNOME With These Simple Tips
Some basic and some interesting GNOME customization tips to get more out of your Ubuntu 18.04 desktop.
Use
Filesytem Navigation
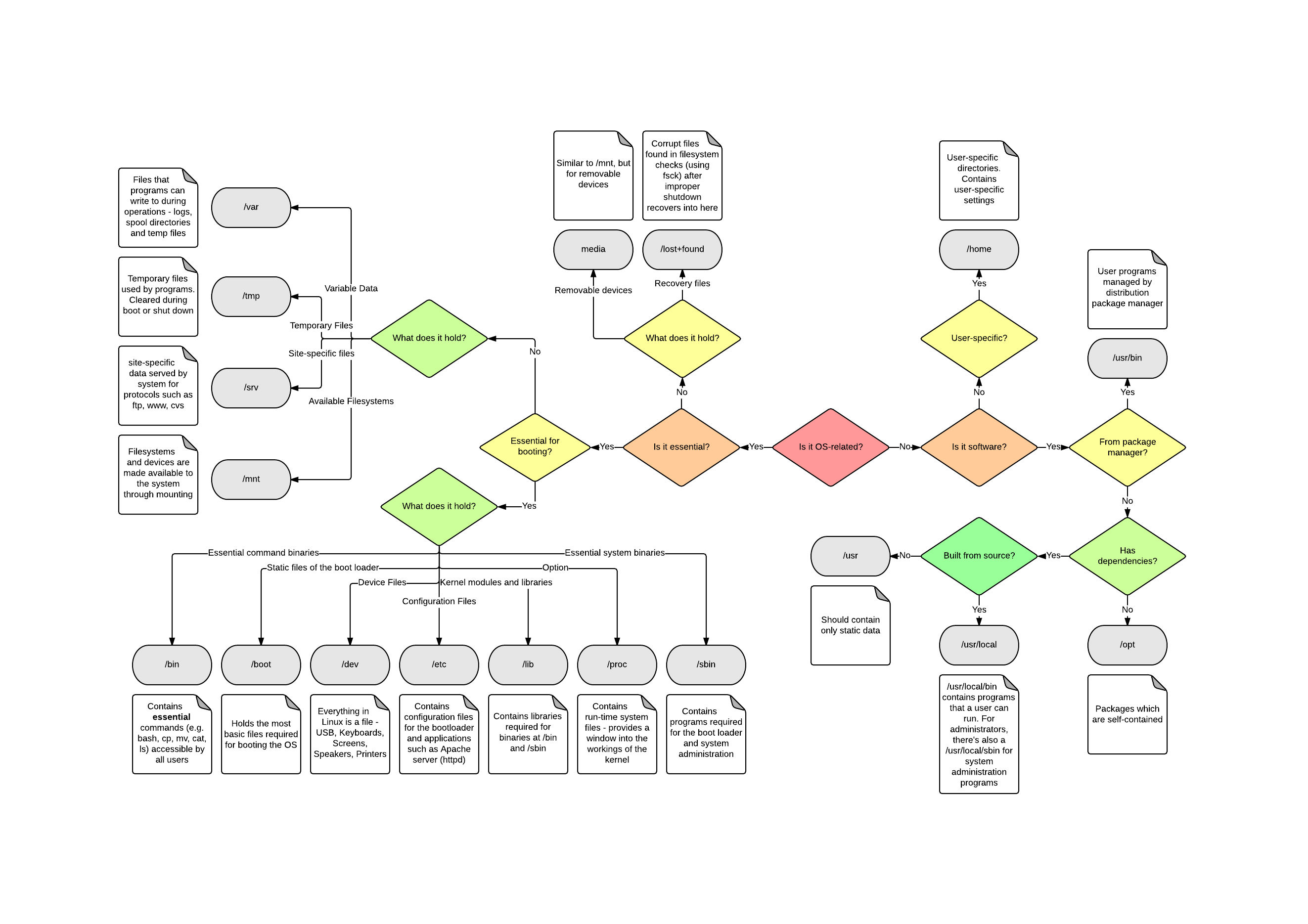
4.9. /usr/local : Local hierarchy /usr/bin vs /usr/local/bin on Linux
Why are there so many places to put a binary in Linux? There are at least these five: /bin/ /sbin/ /usr/bin/ /usr/local/bin/ /usr/local/sbin/ And on my office box, I do not have write permissions… HomeFolder hier - description of the filesystem hierarchy
- Linux Tutorial - 2. Master File System Navigation
This section of the Linux tutorial introduces the basics of the Linux filesystem and commands used to move around it. Also discusses absolute and relative paths.
- LinuxFilesystemTreeOverview
/binis a place for most commonly used terminal commands, like ls, mount, rm, etc./bootcontains files needed to start up the system, including the Linux kernel, a RAM disk image and bootloader configuration files./devcontains all device files, which are not regular files but instead refer to various hardware devices on the system, including hard drives./etccontains system-global configuration files, which affect the system’s behavior for all users./homehome sweet home, this is the place for users’ home directories./libcontains very important dynamic libraries and kernel modules/mediais intended as a mount point for external devices, such as hard drives or removable media (floppies, CDs, DVDs)./mntis also a place for mount points, but dedicated specifically to “temporarily mounted” devices, such as network filesystems./optcan be used to store additional software for your system, which is not handled by the package manager./procis a virtual filesystem that provides a mechanism for kernel to send information to processes./rootis the superuser’s home directory, not in/home/to allow for booting the system even if/home/is not available./runis a tmpfs (temporary file system) available early in the boot process where ephemeral run-time data is stored. Files under this directory are removed or truncated at the beginning of the boot process. (It deprecates various legacy locations such as/var/run,/var/lock,/lib/init/rwin otherwise non-ephemeral directory trees as well as/dev/. > *and/dev/shmwhich are not device files.)/sbincontains important administrative commands that should generally only be employed by the superuser./srvcan contain data directories of services such as HTTP (/srv/www/) or FTP./sysis a virtual filesystem that can be accessed to set or obtain information about the kernel’s view of the system./tmpis a place for temporary files used by applications./usrcontains the majority of user utilities and applications, and partly replicates the root directory structure, containing for instance, among others,/usr/bin/and/usr/lib./varis dedicated to variable data, such as logs, databases, websites, and temporary spool (e-mail etc.) files that persist from one boot to the next. A notable directory it contains is /var/log where system log files are kept.
Encrypted Home Folders
How to decrypt a Ubuntu 16.10 encrypted home folder?
I have a defunct Ubuntu 16.10 installation* on a separate hard drive. There are files on that drive, in my home directory, that I need access to, but are encrypted using Ubuntu’s “encrypt home fold… Encrypted folders on Ubuntu Linux using eCryptfs on an external ha… This blog post continues my Ubuntu encryption tools testing. Previously there was an example for losetup. However, with the latest Ubuntus eCryptfs is recommended instead. eCrypfs makes one directory in a file-system crypted. Since it does not work on a partition level, you d…
Prevent Overheating
- Ubuntu: install the meta-package linux-tools-generic
- Prevent Your Laptop From Overheating With Thermald And Intel P-Sta…
- Psensor
It can monitor: the temperature of the motherboard and CPU sensors (using lm-sensors). the temperature of the NVidia GPUs (using XNVCtrl). the temperature of ATI/AMD GPU
- Most Effective Ways To Reduce Laptop Overheating In Linux - It’s FOSS
- How to control fan speed?
- Intel Temperature Guide
Update: Oct 9, 2019 Intel Temperature Guide - by CompuTronix Preface The topic of processor temperatures can be very confusing. Conflicting opinions based on misconceptions concerning terminology, specifications and testing leaves users uncertain of how to properly check …
Shell
- How do I restore .bashrc to its default?
typing source /etc/environment will fix path for the moment, then you can replace
.bashrcand.profile - Processing Text with Linux Shell - Part 1 Using sed command to efficiently process text files in linux
- Syslog : The Complete System Administrator Guide – devconnected
Complete Guide on understanding the Syslog protocol, syslog message format as well as log forwarding. Best practices included!
- Learn Enough Command Line to Be Dangerous - Introduction to the Unix command line.
- Mac (Bash) to Windows (Command Prompt) mappings
- The Unix Shell - Introducing the Shell
- Bash Beginners Guide
This is a practical guide which, while not always being too serious, tries to give real-life instead of theoretical examples. I partly wrote it because I don’t get excited with stripped down and over-simplified examples written by people who know what they are talking about, showing some really cool Bash feature so much out of its context that you cannot ever use it in practical circumstances. You can read that sort of stuff after finishing this book, which contains exercises and examples that will help you survive in the real world.
- http://www.hypexr.org/bash_tutorial.php
- The Bash Academy
- The new Windows Terminal
- TIL: A preceding space prevents dangerous commands from going into history
- Better bash history search with McFly
- How to Bookmark commands in Terminal
- Learning the shell - Lesson 3: Looking around
- 51 Useful Lesser Known Commands for Linux Users
- Why you should learn just a little Awk - An Awk tutorial by Example
- 10 simple Linux tips which save 50% of my time in the command line
- AWK command in Unix/Linux with examples - GeeksforGeeks
- Processing Text with Linux Shell - Part 2
- dylanaraps/pure-bash-bible
- 15 Practical Grep Command Examples In Linux / UNIX
- How to Save a File in Vi / Vim Editor in Linux
Scripting
- Shell Scripting Tutorial
This tutorial is written to help people understand some of the basics of shell script programming (aka shell scripting), and hopefully to introduce some of the possibilities of simple but powerful programming available under the Bourne shell. As such, it has been written as a…
- How to write idempotent Bash scripts
ZSH
- Oh My Zsh - a delightful & open source framework for Zsh
- How to Setup ZSH and Oh-my-zsh on Linux
- robbyrussell/oh-my-zsh
Networking
- https://netfilter.org/documentation/HOWTO//networking-concepts-HOWTO-2.html
- How to set a Static IP in Ubuntu – Ubuntu Network Confirguration
- How to Find What Devices are Connected to Network in Linux - It’s FOSS Setting up an ad-blocking VPN with Wireguard and Pihole
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Internet/ConnectionSharing
- Connect two computers with SSH in a home LAN
- I have two ubuntu computer shared the same wifi and desire to reach another from one’s terminal. First create an user on the second computer named “Second” and hostname “Algorithms” Then tried to
- Nutty Nutty is a Network Utility made for elementary OS
- How To Set Up a Firewall with UFW on Ubuntu 18.04
- By default, Ubuntu comes with a firewall configuration tool called UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall). UFW is a user-friendly front-end for managing iptables firewall rules and its main goal is to make managing iptables easier or as the name says uncomplicated.
- Linux Server
- EtherApe
- EtherApe is a graphical network monitor modeled after etherman. Featuring Ethernet, IP, TCP, FDDI, Token Ring and wireless modes, it displays network activity graphically.
- https://twitter.com/qw5kcmv3/status/1188145406200500230?s=12
This week we discussed tunneling with SSH, so I feel it is appropriate to highlight this great book dedicated to SSH. You think you know how to use all the features of SSH, but you don’t, and Googling isn’t going to provide you this comprehensive compilation. #DailyBookDrop
- bryanpkc/corkscrew
- A tool for tunneling SSH through HTTP proxies. Contribute to bryanpkc/corkscrew development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Introduction to Linux Hardening
Tools
- Some Awesome Linux Tools To Make Your Tech Life Easier
- My Favorite Linux Tools
- Libre Lounge: 27: Cool Tools of Summer ‘19 on Apple Podcasts
- Top 15 Linux Data Recovery Tools: The Professionals’ Choice Linux data recovery tools are inseparable parts to the Linux users for preserving their data securely surpassing unexpected failure of hard disk.
- https://kdenlive.org/en/ Kdenlive is an acronym for KDE Non-Linear Video Editor. It is primarily aimed at the GNU/Linux platform but also works on BSD and MacOS. It is currently being ported to Windows as a GSOC project.
- crontab.guru - the cron schedule expression editor An easy to use editor for crontab schedules.
Editors
- Setup VS Code for Efficient PHP Development
- PacVim – PacVim is a game that teaches you vim commands
- “Damn! Now I have to use Vim”
- History and Effective Use of Vim
Version Management
- https://rvm.io/integration/bundler
- Version Management for Ruby, Python, Node and Rust
- How To Install Ruby on Rails with rbenv on Ubuntu 18.04